Istio CLI Cheat Sheet for Ops

This page is a collection of istioctl commands for debugging and troubleshooting Istio. I gathered them from various sources and my own experience. Happy to get feedback and to complete this page with even more nice commands!
| Use the navigation menu on the right side to jump to a specific section. |
Install istioctl
Install the Istio CLI and add it to the PATH
ISTIO_VERSION=1.17.2
curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | ISTIO_VERSION=${ISTIO_VERSION} TARGET_ARCH=x86_64 sh -
export PATH=$PWD/istio-${ISTIO_VERSION}/bin:$PATHInstall Istio
Make sure to distinguish the IstioOperator CRD from the Istio Operator. The Istio Operator is a Kubernetes operator that manages the Istio installation, and its use is now discouraged. The IstioOperator CRD is a Kubernetes CRD that defines the Istio installation. The IstioOperator CRD works well with istioctl.
IstioOperator CRD = ❤️
Istio Operator = 💔 (now discouraged)
One-liner
istioctl install -y -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
spec:
profile: default
hub: docker.io/istio
tag: 1.17.2
revision: 1-17
defaultRevision: true
meshConfig:
accessLogFile: /dev/stdout
EOFPost-install check-up
istioctl verify-install -r 1-17Istio profiles
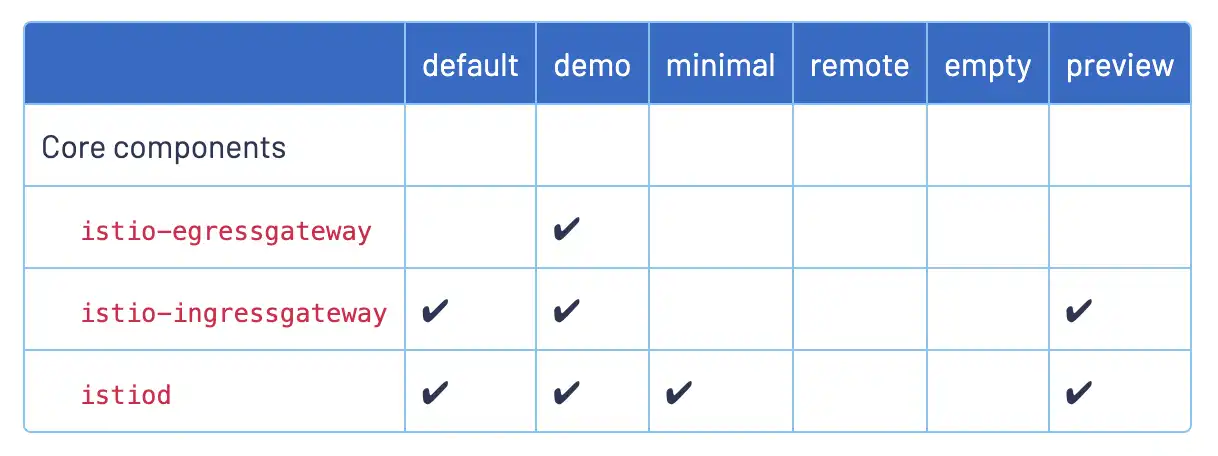
For testing purpose, Istio offers several profiles:
If not specified in the IstioOperator CRD, the default profile is used.
|
It is recommended to use several IstioOperator CRDs, to manage istiod and the gateways separately. A good practice consists of using the minimal profile for istiod, and additional IstioOperator CRDs for the N/S and E/W gateways. |
Anatomy of the IstioOperator CRD
The API Reference for the IstioOperator CRD is here.
Two main sections:
-
components:defines the Istio components to install -
meshConfig:defines the mesh configuration for both the control-plane and the data-plane.
Revisions
Using Istio revisions is a good practice if you want to do canary upgrades. It allows you to have multiple versions of Istio installed in parallel and to switch between them.
List revisions
istioctl x revision listCanary upgrade with revisions
The following code snippet shows how to do a canary upgrade of the Istio control-plane using revisions. It assumes that you have already installed Istio 1.17 with the defaultRevision: true option and also that you have already installed Istio 1.18 with the revision: 1-18 option.
# Current version is using revision 1-17
# Canary upgrade the "test-ns" namespace to revision 1-18
kubectl label namespace test-ns istio-injection- istio.io/rev=1-18 --overwrite
kubectl rollout restart deployment -n test-ns
# check if everything is ok, then switch the default revision to 1-18
istioctl x revision default 1-18Delete old revision
# uninstall the old revision
istioctl uninstall --revision 1-17 -ySidecar injection
Sidecar injection at the namespace level
kubectl label namespace test-ns istio-injection=enabled
# - or -
kubectl label namespace test-ns istio.io/rev=1-17Manual sidecar injection for workloads
istioctl kube-inject -f samples/sleep/sleep.yaml -r 1-17 | kubectl apply -f -Observe
Metrics
istioctl dashboard prometheus
istioctl dashboard grafanaTraces
istioctl dashboard kiali
istioctl dashboard jaegerLogs
Enable access logs on sidecars
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: telemetry.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: Telemetry
metadata:
name: mesh-default
namespace: istio-system
spec:
accessLogging:
- providers:
- name: envoy
EOFPlay with the control-plane
Change the log level
# change the log level
istioctl admin log --revision 1-17 --level authorization:debug
# check
istioctl admin log --revision 1-17Get the logs
kubectl logs $(kubectl -n istio-system \
get pods -l app=istiod -l istio.io/rev=1-17 \
-o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') \
-c discovery -n istio-systemControl-plane metrics
kubectl exec deploy/istiod-${ISTIO_REVISION} -n istio-system -- curl localhost:15014/metrics -sView discovered services
export ISTIO_REVISION=1-17
kubectl exec -n istio-system deploy/istiod-${ISTIO_REVISION} \
-- pilot-discovery request GET /debug/registryz | jq '.[].hostname' | sortDump Istio config
Find all the Istio resources that you have created and also the EnvoyFilters that Istio has generated:
export ISTIO_REVISION=1-17
kubectl -n istio-system exec -it \
$(kubectl -n istio-system get pods -l app=istiod -l istio.io/rev=${ISTIO_REVISION} \
-o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') \
-- curl http://localhost:8080/debug/configz | jqPrint istiod version
kubectl exec deploy/istiod-${ISTIO_REVISION} \
-n istio-system -- curl localhost:15014/version -sCertificate management
Retrieve the client certificate assigned to a workload
istioctl pc secret deploy/sleep -o json \
| jq '[.dynamicActiveSecrets[] | select(.name == "default")][0].secret.tlsCertificate.certificateChain.inlineBytes' -r \
| base64 -d \
| openssl x509 -noout -textFetch the root CA
kubectl get cm istio-ca-root-cert -o json | jq '[.data[]][0]' -r | openssl x509 -noout -text
# or
kubectl --context="${CTX_CLUSTER1}" get secret cacerts -n istio-system -o jsonpath='{.data.root-cert\.pem}' | base64 -d | openssl x509 -noout -text
# similarly for the CA certificate (intermediate certificate)
kubectl --context="${CTX_CLUSTER1}" get secret cacerts -n istio-system -o jsonpath='{.data.ca-cert\.pem}' | base64 -d | openssl x509 -noout -textCompare CAs
Sometimes, it’s very useful to compare the CA that was shared with a pod, with the root CA given to Istio.
It makes even more sense for in a multi-cluster setup.
istioctl pc rootca-compare deploy/sleep.default deploy/istio-ingressgateway.istio-system
# multi-clusterTroubleshoot
Look for config errors
istioctl analyze -A --revision 1-17Check the sync status
istioctl proxy-statusChange the log level (data-plane)
istioctl proxy-config log deploy/httpbin --level debug
istioctl pc log -n istio-gateways deploy/istio-ingressgateway --level debug
# or on a per-component basis
istioctl pc log deploy/httpbin --level connection:debug,conn_handler:debug,filter:debug,router:debug,http:debug,upstream:debug
# list of the Envoy log components:
https://github.com/envoyproxy/envoy/blob/55e9b316d2e7d17a05b68924d0dffc2635ab8e52/source/common/common/logger.h#L29Proxy stats
Cluster stats
# Ingress Gateway
istioctl x envoy-stats -n istio-gateways deploy/istio-ingressgateway --type clusters
# - or - more advanced query
kubectl -n istio-system exec -it deploy/istio-ingressgateway \
-- curl localhost:15000/clusters \
| grep httpbin \
| grep rq_total
# Works the same with regular workloads
istioctl x envoy-stats -n default deploy/sleep --type clustersStats as Prometheus metrics
kubectl -n default exec -it deploy/sleep -c istio-proxy \
-- curl localhost:15000/stats/prometheus \
| grep istio_requests_totalInspect
My favorites when it comes to debugging!
Find out which policies are applied
# Find AuthorizationPolicies
istioctl x authz check deploy/httpbin.default
# Check the mTLS mode for this workload (STRICT or PERMISSIVE)
istioctl x describe pod httpbin-69ff487f4b-25mzh -n default[Fav] View the Gateway listeners and routes
Essentially for the Ingress Gateway:
# Listeners
istioctl -n istio-system pc l deploy/istio-ingressgateway
# more info with the following:
istioctl -n istio-system pc l deploy/istio-ingressgateway --port 8443 --type HTTP -o json
# Routes
istioctl -n istio-system pc r deploy/istio-ingressgateway[Fav] View the upstream clusters and endpoints
Check what clusters and endpoints are known by a proxy (or gateway):
# Clusters
istioctl pc c deploy/httpbin -n default --fqdn sleep.default.svc.cluster.local -o json
istioctl pc c deploy/istio-ingressgateway.istio-system --fqdn httpbin.org -o json
# Endpoints
istioctl pc endpoints deploy/httpbin -n default --cluster "outbound|80||sleep.default.svc.cluster.local" -o json
istioctl pc endpoints deploy/istio-ingressgateway.istio-system --cluster "outbound|443||httpbin.org" -o jsonFull config dump for a proxy
kubectl exec $(kubectl get pods -l app=httpbin -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') \
-c istio-proxy -- pilot-agent request GET config_dump